By Gillian Yeend (UniSA) and Kristy Newton (UOW)
As higher education has increasingly embraced digital and hybrid learning experiences, it is important that students are able to seamlessly navigate the spaces they use for learning. Libapps Learning Tools Interoperability (LTI) embeds Libguides into the Learning Management System (LMS). The University of South Australia (UniSA) and University of Wollongong (UOW) have recently used this tool. Their experience demonstrates how integrating Library resources into the LMS improves access and discovery. Both Universities use Moodle as the LMS.
Background to use of Libguides at UniSA and UOW
UniSA Library has used the Libguides software developed by SpringShare since 2011. Currently they have 82 guides including subject, teaching, and research guides. The guides assist students, teaching and research staff to find the specific information they need. Some courses have individual assignment helps located on the subject guides. Before the use of the tool, students had to move out of their course site to access the guides.
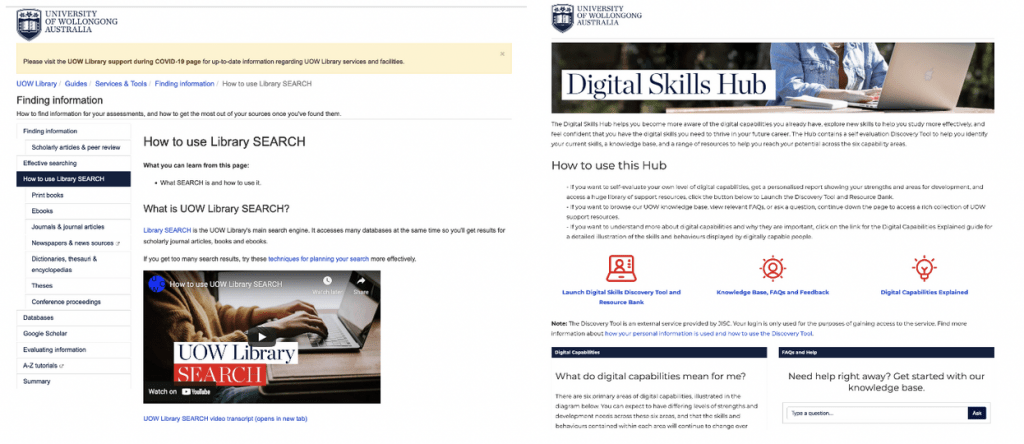
UOW has also been using the LibGuides software since 2010, and currently has 55 Guides for Library subject information, teaching, and research skills. The Guides are primarily accessible via the Library website, with some being embedded in individual Moodle sites manually. In 2021 UOW designed a Digital Skills Hub within Libguides to support the digital skills of students both while at University and preparing them for their future careers. The Hub is embedded in the LMS using LTI integration.
Challenge of discovery and the student experience
Students can find it difficult to locate key information amongst the plethora of online sources. In the course of their studies, students need to be able to navigate across course information and material in the LMS, academic information resources via the Library, as well as a variety of other platforms used for institutional communication. This context, with the addition of diverse digital and academic literacies, means that there are challenges inherent in navigating these online information environments which is often expressed in terms of cognitive load. Mayer’s cognitive theory of multimedia learning highlights this challenge. Learners “…must use their limited processing capacity to select important information, [and] organize it into a coherent structure in working memory” (Mayer & Fiorella, 2022, pg 183).
One of the five principles for reducing extraneous processing is signaling. This theory posits that “…people learn more deeply … when cues are added that guide attention to the relevant elements of the material or highlight the organization of the essential material” (Mayer & Fiorella, 2022, pg 221). Integration of library guides within the course site can ease the cognitive load. Key information is located where it is applicable and accessible. In a nutshell, it makes sense to place the key information in a place that students are already using for learning!
LTI: what is it, and how does it address the challenge?
UniSA
In 2020 the UniSA Library conducted a pilot project within UniSA Online over one study period (just over two months). The aim was to improve the integration of library guides and assignment helps into the online learning environment using the LTI. The LTI allowed Course Coordinators to manually embed a range of Library guide content where relevant. Students could access the guides without leaving their course site.
During the pilot 12 UniSA Online courses embedded 18 Libguide objects. Assignment helps were the most popular option. A total of 3168 hits were recorded. The pilot project demonstrated the benefits of the tool with:
- Improved access- 93% of access to one assignment help was through the embedded content as opposed to the library website for the same period.
- Improved engagement- students were actively returning to the content.
- Ease of use- Course Coordinator feedback was positive. All indicated that they would recommend this feature and were confident to embed.
Due to the success, Library rolled out the LTI to feature across all UniSA courses in the following year. A further enhancement used the Automagic LTI tool. Subject guides linked in course sites were automatically displayed as an embedded guide. This enhancement removed the reliance on Course Coordinators to manually embed. This ensured equitable access for all students.
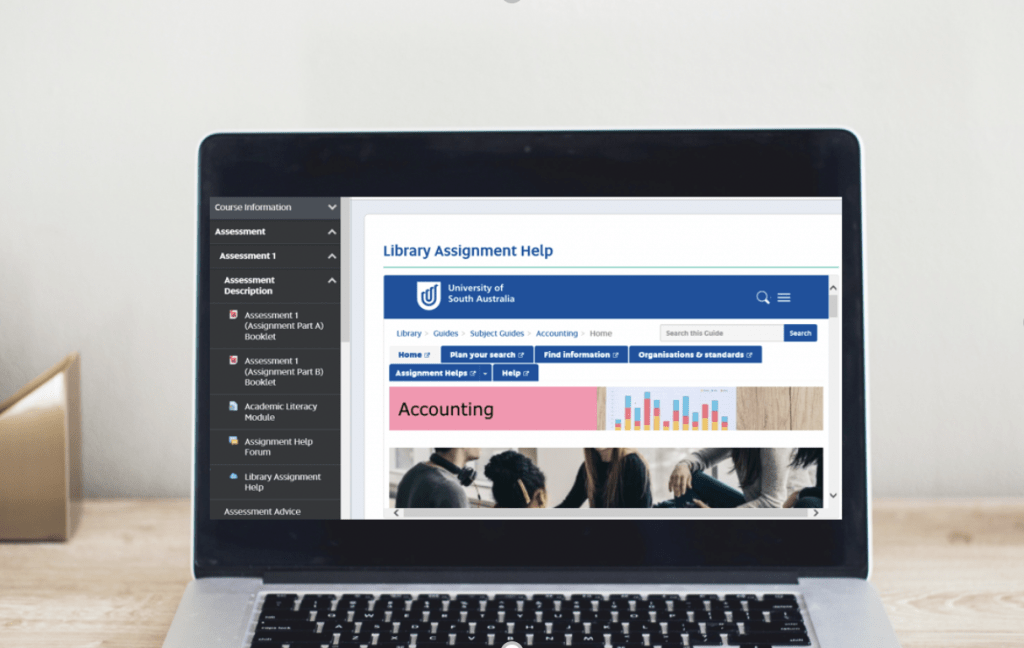
UOW
Like UniSA, UOW used the Automagic LTI tool to add the Digital Skills Hub content into the LMS across the University. The ability to embed within the LMS was a key factor in choosing LibGuides as the platform for the creation of the Digital Skills Hub, as it was important that the Hub was available equitably with minimal impact on academic staff. Ensuring digital skills support was in a location that students already frequented was ideal.
Using LTI to embed the content within Moodle also meant that the resource did not need to be consistent with existing subject LibGuides. The Library applied custom CSS to create a resource consistent with University branding. The Library’s subject-based LibGuides are visually identifiable as a Library resource, but in creating the Digital Skills Hub it was important that the Hub be seen as a whole-of-institution resource, rather than a Library resource.
As the Digital Skills Hub was recognised as strategically important, the project secured support from the Learning, Teaching and Curriculum unit to insert the LTI link into all existing Moodle subject sites. New sites created which use the institutional template will automatically include the link to the Hub. Since it was launched in February 2022, the Digital Skills Hub has been accessed over 9000 times.
What we learned
The LTI tool at both UniSA and UOW has been invaluable. It has ensured library support is where it needs to be, easing the cognitive load for students and minimising the burden on academic staff to provide targeted support content.
References
Mayer, RE & Fiorella, L 2022, The Cambridge handbook of multimedia learning / edited by Richard E. Mayer, University of California, Santa Barbara, Logan Fiorella, University of Georgia., Third edition., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
