By Bryony Hawthorn, Information Services Manager, University of Waikato Library, bryony.hawthorn@waikato.ac.nz
Background
The University of Waikato Library has been using a live chat service successfully for more than 14 years. This is a very popular service with students – and that was even before the pandemic flipped our lives upside down!
In 2019 library staff numbers were reduced, and we realised we may not always be able to staff the live chat as we have done in the past. This led to the idea of a chatbot.
Meet our chatbot, Libby
We chose to build our chatbot using the LibraryH3lp platform as we already use this for our live chat service. So bonus = no extra costs! We named our chatbot Libby.
Libby’s interface is similar to live chat so it creates a consistent experience for users. The only difference is the colour: green for live chat and orange for the chatbot.
We create the responses that Libby sends. The chatbot administration back end has been set up to be simple to use and this means library staff creating responses don’t need to be tech experts. We’ve chosen to focus primarily on library-related topics.
Bumpy beginnings
Libby was very basic when we started. We struggled to get her to reply to keywords (the user had to type the EXACT word or phrase we had in our response bank) and she couldn’t return multiple responses to a single question. Because of this, Libby’s most common response was, “Sorry, I could not process your request. Please try a different word or phrase”. Let’s just say it was a bumpy beginning and a frustrating experience for our early users.
Stepping up
The road became a lot smoother when we introduced a natural language toolkit. This included:
● Text filtering – keywords can appear anywhere in a user’s question so no need to type an exact phrase anymore.
● Removing stop words (e.g. a, at, the, not, and, etc).
● Tokenizing – isolates words so they are compared separately.
● Stemming – allows for different endings for keywords.
● Synonyms – increase the range of words that trigger a response.
We also improved the way Libby greets users and made it clear how to receive help from a person. Most recently we added a module to assist with spelling errors.
One of our biggest successes has been introducing a prompt to encourage users to type their email address if they want a follow up from a librarian. Prior to Libby’s introduction, if the chat service was offline, users were told to email the library for assistance. This didn’t happen very often. But now users find it easy to add their email address and thus allow us to contact them. This has markedly increased the number of users receiving further help.
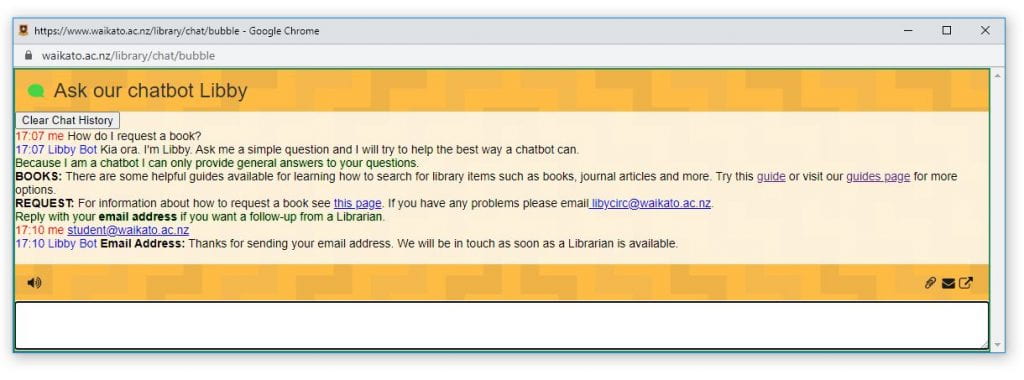
What we learned along the way
● Don’t do it alone. Use those around you with the right technical experience.
● Simple fixes can make a big difference.
● Make it clear to your users they are chatting with a bot who won’t be able to answer everything.
● Make it easy for users to request a follow up from a librarian.
Libby is still a work in progress and our journey is ongoing. Who knows where the road will lead. There are other ways to build a chatbot and some are simpler than what we have done. If you are interested in creating something similar, do look around for options to find something that will suit your needs.
If you’d like to learn more about our journey so far, you can watch our presentation from the LearnFest2021 conference.
